Psalm 45
Introduction
Overview
The purpose was the psalmist's probable intent or reason for writing this psalm. The Content is a concise summary of the whole psalm's content. The Message is the main idea the psalmist probably wanted the audience to remember upon or after hearing the psalm.
Purpose: To celebrate the king (on the occasion of his wedding) for his just and eternal rule.
Content: The king's throne is forever and ever. The king is attractive, wise, powerful, and righteous. The king is due loyalty from his new bride and honour from foreign nations. The king's descendants will be princes. Therefore, the king's throne is forever and ever!
Message: God's chosen king and his descendants rule forever with wisdom, righteousness, and joy.
Background Ideas
Cultural, historical, and contextual information that is important to know to understand this psalm
- Songs in praise of the king (rather than the deity) are common in the ANE, though rare in the biblical psalms. One example is the Egyptian marriage stele of Rameses II, which presents the marriage as as part of a political alliance following a military victory.
- Lips of kindness are associated with wisdom and virtue (Prov 22:1, 11; Ecc 10:12); the ideal ANE king spoke with wisdom.
- The ideal ANE king was a warrior.
- Ancient royal marriages were often political arrangements between one nation and another. The marriage described in this psalm may have been arranged as part of a political alliance between Isreal/Judah and a neighbouring state (such as Tyre). The NET Bible translates Heb. "your people" (v. 11) as "your homeland" to reflect this situation.
Background Situation
A brief explanation of the "story behind" the psalm--what was going on in the psalmist's life, and/or Israel's history, that prompted the psalmist to pen this psalm? The colors in the boxes correspond to the participants in the psalm (see Participant Analysis).
Sections
These sections divide the content of the psalm into digestible pieces , and are determined based on information from many of our layers, including Semantics, Poetics, and Discourse. The columns, left to right, contain: the verse numbers; the main title of the section; a brief summary of the content of that section (quote marks indicate the text is taken directly from the English text of the psalm (as per our Close-but-Clear translation)); and an icon to visually represent and remember the content.
Videos
The Overview video is a brief, concise explanation of the psalm, pulling all the most important information specific to this psalm from each of our analytical layers. The video begins with a high-level, birds-eye view of the content of the psalm, then explores and explains the psalm verse by verse. Relevant contextual information is also included. No Hebrew knowledge required--this video serves as an entry point for all users to all our other information about the psalm.
Video files
- The script for the Overview video is available here.
- The slides for the Overview video are available here.
Translation Aids
Recommended steps for translating the psalms
To translate poetry accurately and beautifully, a knowledge of both the source language's poetry and the target language's poetry is needed. So, here are the steps we recommend to follow when setting out to translate the psalms:
- GAIN AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE TARGET LANGUAGE'S POETRY/ARTS. Research and analyze many examples from numerous genres of poetry, storytelling, and music in the target language and culture, and document findings. See our for help.
- GAIN AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE SOURCE LANGUAGE'S (HEBREW) MEANING AND POETRY. The aim of all our materials is to provide exactly this for the translator, poet/musician/artist, and consultant: an understanding of what the psalm means, as well as its poetics.
- TRANSLATE THE PSALM IN THE APPROPRIATE LOCAL ART/POETRY GENRE.
Translation and Performance Notes
TPNs are an at-a-glance reference for anyone involved with translating or checking a translation of the psalm. Specific words, phrases, and images that could be difficult to understand or to translate are highlighted, and then briefly discussed. Each note is intended to help the reader understand the meaning of the Hebrew word or phrase in its context, as well as provide a few translation options or suggestions, often pulling from existing translations. Where pertinent, our preferred translation option is given. NOTE: These notes are intended to supplement a robust internalization of the psalm, not replace it. Translation Challenges for Psalm 45 not available yet.
Close-but-Clear Translation
The Close-but-clear translation (CBC) exists to provide a window into the Hebrew text according to how we understand its syntax and word-to-phrase-level semantics. It is designed to be "close" to the Hebrew, while still being "clear." Specifically, the CBC encapsulates and reflects the following layers of analysis: grammar, lexical semantics, phrase-level semantics, and verbal semantics. It does not reflect our analysis of the discourse or of poetics. It is not intended to be used as a stand-alone translation or base text, but as a supplement to Layer-by-Layer materials to help users make full use of these resources.
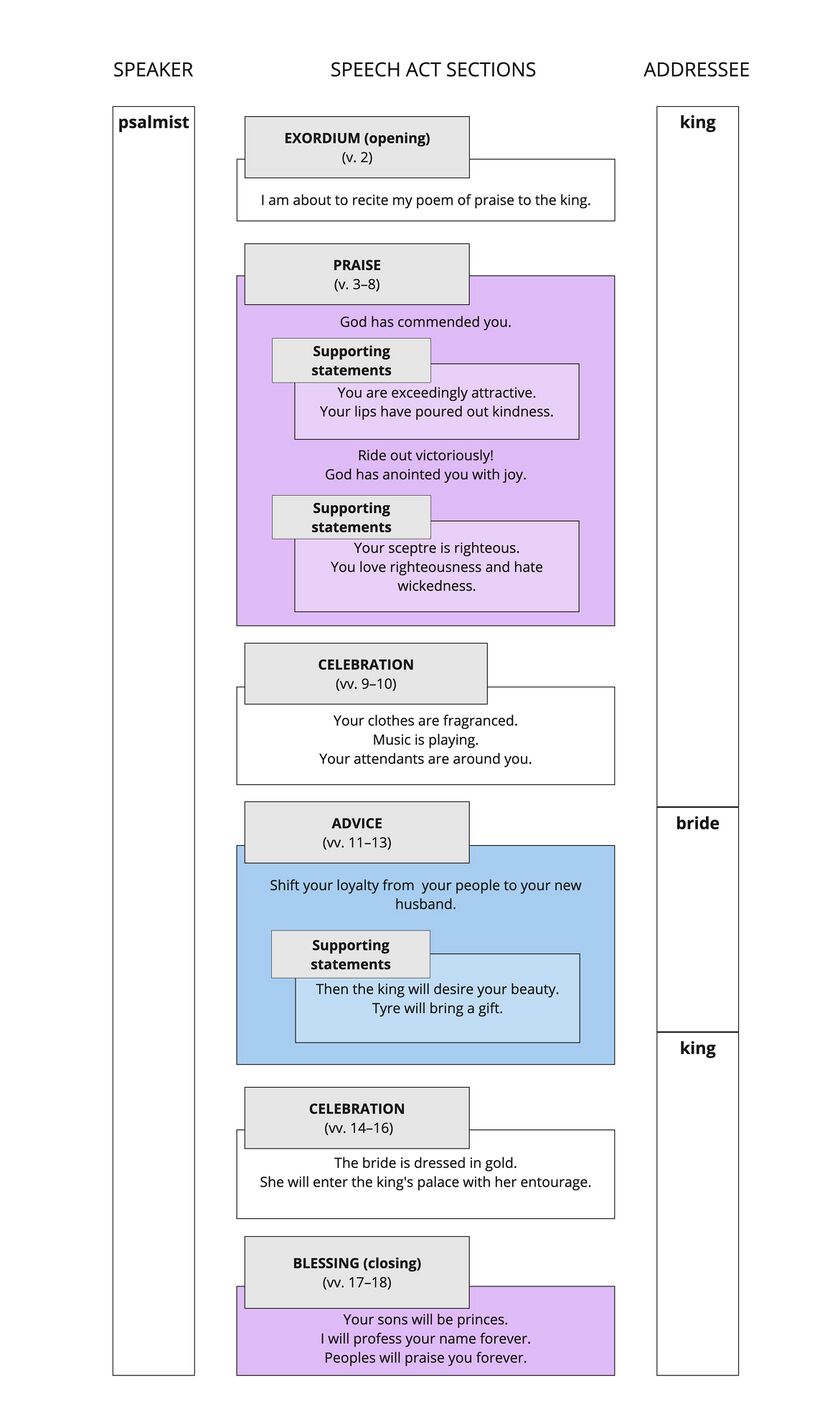
- 1. For the director. According to “Lilies.” By the Korahites.
- A maskil. An ode.
- 2. My heart has been stirred by a good theme;
- I am about to recite my verses to the king.
- My tongue is a pen of a skilful scribe.
- 3. You are the most attractive of all people;
- kindness has been poured out by your speech.
- Therefore, God has commended you forever.
- 4. Strap your sword upon your thigh, great one,
- in your splendour and your majesty.
- 5. And in your majesty, victoriously ride
- for the cause of truth and humility, righteousness,
- and let your right hand show you awesome things.
- 6. Your arrows are sharp.
- Peoples will fall under you;
- in the heart of the enemies of the king.
- 7. Your throne, God, is forever and ever;
- the sceptre of your kingdom is the sceptre of righteousness.
- 8. You love righteousness, and you hate wickedness.
- Therefore, God, your God, has anointed you
- with the oil, which is rejoicing, more than your companions.
- 9. All your clothes are myrrh and aloes [and] cassia.
- From ivory palaces, stringed instruments have caused you to rejoice.
- 10. Princesses are among your treasures;
- a queen has taken a stand at your right hand in the gold of Ophir.
- 11. Hear, daughter, and see and incline your ear,
- and forget your people and your father’s household,
- 12. so that the king will desire your beauty,
- because he is your husband, and bow down to him,
- 13. and Daughter Tyre, the richest of people, will seek your favour with a gift.
- 14. The princess is in her chamber with all kinds of valuable goods;
- her clothing [is made] from gold settings.
- 15. In embroidered cloth she will be led to the king;
- young women after her, her female companions,
- being brought to you.
- 16. They will be led with joy and gladness;
- they will go into the king’s palace.
- 17. In the place of your ancestors, your sons will be [princes];
- you will appoint them as princes over all the earth.
- 18. I shall profess your name in all generations.
- Therefore peoples will praise you forever and ever.
Explore the Layers
Exegetical Issues
The Hebrew of the psalms can be difficult to understand at times. In this section, you can explore (in either video or text format) what we've deemed to be the three most important difficulties in the Hebrew, and follow our reasoning as we do a deep dive in scholarly work and explain our conclusions.
Exegetical Issues for Psalm 19:
- The Syntax of Psalm 45:6 (Draft)
- The Syntax and Participants of Psalm 45:7a (Draft)
- The Text and Grammar of Psalm 45:12–13 (Draft)
Grammar
A full, detailed diagram showing the grammatical function of each word/morpheme in the Hebrew text, along with accompanying notes.
Semantics
Lexical and Phrase-level Semantics
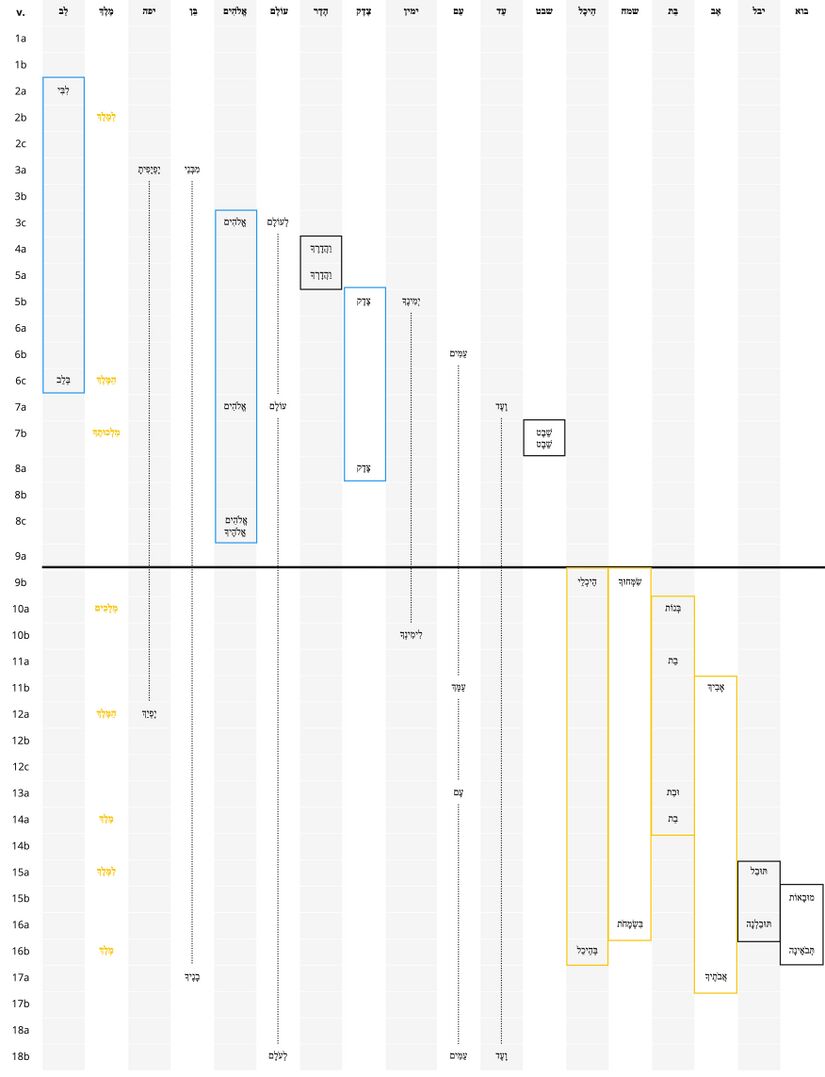
Lexical semantics is the study of word meanings. It examines semantic range (=possible meanings of a word), the relationship between words (e.g. synonymy, hyponymy), as well as the relationship between words and larger concepts (conceptual domains). One component of our approach involves not only the study of the Hebrew word meaning, but also of our own assumptions about word meaning in modern languages. Because the researcher necessarily starts with their own cultural assumptions (in our case, those of Western-trained scholars), this part of the analysis should ideally be done afresh for every culture. Phrase-level semantics analyses the meaning of syntactic units which are larger than the level of the word and smaller than the level of the clause. Specifically, this layer analyses the meaning of prepositional phrases , construct phrases (a special type of construction in Hebrew), phrases formed by a coordinating waw conjunction, and noun phrases which consist of a noun plus a determiner (such as "the") or a quantifier (such as "all").
Verbal Semantics
Verbal Semantics focuses on the relationship between verbs, time and modality, and gives details about each verb in the psalm. This is important for interpretation and translation, and how one analyses a verb can have a significant effect on how it is rendered.
Story Behind the Psalm (Unit-level Semantics)
The Story Behind triangle tells the "story" (reading from left to right, beginning at the bottom left corner) of what might have prompted the psalmist to write this psalm. The events and ideas on the triangle are taken from the Propositions and Assumptions table below. Propositional content is the part of the meaning of a clause or sentence that is constant, despite changes in such things as voice, illocutionary force, tense/aspect/mode, person/gender/number, etc. It refers to “the kind of situation or event described by the underlying proposition.” Once we have identified the propositional content, we ask, “what would the world have to be like for this [proposition] to be true?” That is, what does this proposition presuppose about the world? What does it entail? What might be implied? In what kind of situation does this make sense? In other words, what assumptions are bound up with this proposition? We distinguish three kinds of assumptions:
- Common-ground assumptions
- Local-ground assumptions
- Playground assumptions
See the Legend accompanying the chart for more details on the types of assumptions.
Understanding the assumptions involved will help translators understand the implicit information present in the text, so that they can decide which of these to make explicit in the translation or biblical helps for their audience to understand the text's larger meaning.Discourse
Participant Analysis
This layer examines each participant in the psalm, whether they have speaking roles in the psalm, or are just referenced in the poem. Often, the relationships and interactions among participants sheds much light on the understanding and translation of a psalm. The summary visuals give a view of the participants in the psalm as a whole, while the tables list the participant information for each clause.
Macrosyntax
Speech Act Analysis
Emotional Analysis
Repeated Roots
Poetics
Poetic Structure & Features
Verse-by-Verse Notes
View all of Psalm 45 Verse-by-Verse Notes, or click on an individual verse below.