Psalm 1 Story Behind
About the Story Behind Layer
The Story Behind the Psalm shows how each part of the psalm fits together into a single coherent whole. Whereas most semantic analysis focuses on discrete parts of a text such as the meaning of a word or phrase, Story Behind the Psalm considers the meaning of larger units of discourse, including the entire psalm.
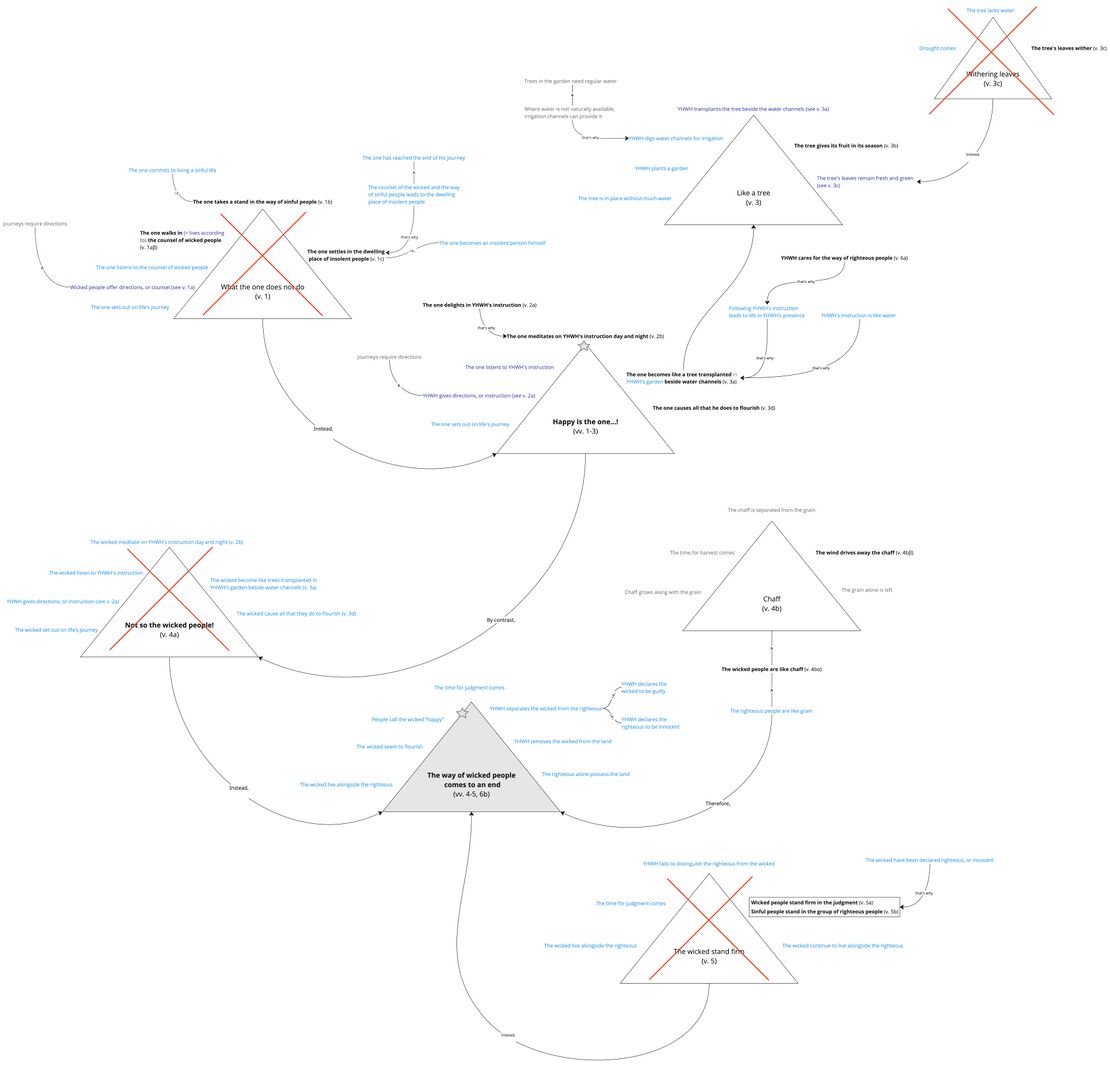
The goal of this layer is to reconstruct and visualize a mental representation of the text as the earliest hearers/readers might have conceptualized it. We start by identifying the propositional content of each clause in the psalm, and then we identify relevant assumptions implied by each of the propositions. During this process, we also identify and analyze metaphorical language (“imagery”). Finally, we try to see how all of the propositions and assumptions fit together to form a coherent mental representation. The main tool we use for structuring the propositions and assumptions is a story triangle, which visualizes the rise and fall of tension within a semantic unit. Although story triangles are traditionally used to analyze stories in the literary sense of the word, we use them at this layer to analyze “stories” in the cognitive sense of the word—i.e., a story as a sequence of propositions and assumptions that has tension.
Summary Triangle
The story triangle below summarises the story of the whole psalm. We use the same colour scheme as in Participant Analysis. The star icon along the edge of the story-triangle indicates the point of the story in which the psalm itself (as a speech event) takes place. We also include a theme at the bottom of the story. The theme is the main message conveyed by the story-behind.
| Story Triangles legend | |
|---|---|
| Propositional content (verse number) | Propositional content, the base meaning of the clause, is indicated by bold black text. The verse number immediately follows the correlating proposition in black text inside parentheses. |
| Common-ground assumption | Common-ground assumptions[1] are indicated by gray text. |
| Local-ground assumption | Local-ground assumptions[2] are indicated by dark blue text. |
| Playground assumption | Playground assumptions[3] are indicated by light blue text. |
| The point of the story at which the psalm takes place (as a speech event) is indicated by a gray star. | |
| If applicable, the point of the story at which the psalm BEGINS to take place (as a speech event) is indicated with a light gray star. A gray arrow will travel from this star to the point at which the psalm ends, indicated by the darker gray star. | |
| A story that repeats is indicated by a circular arrow. This indicates a sequence of either habitual or iterative events. | |
| A story or event that does not happen or the psalmist does not wish to happen is indicated with a red X over the story triangle. | |
| Connections between propositions and/or assumptions are indicated by black arrows with small text indicating how the ideas are connected. | |
| Note: In the Summary triangle, highlight color scheme follows the colors of participant analysis. | |
Background ideas
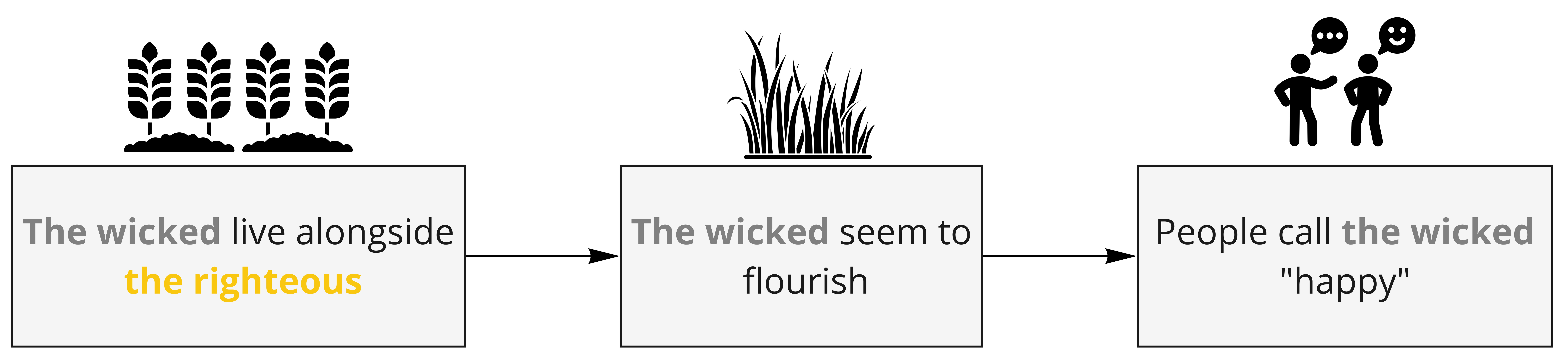
Following are the common-ground assumptionsCommon-ground assumptions include information shared by the speaker and hearers. In our analysis, we mainly use this category for Biblical/Ancient Near Eastern background. which are the most helpful for making sense of the psalm. Psalm 1 (especially when it is read against the background of the end of Malachi) appears to assume a situation in which...
- The wicked live alongside the righteous (like grain and chaff growing together in a field)
- The wicked seem to flourish (cf. Mal 3:14-15)
- People call the wicked "happy" (cf. Mal 3:14-15)
In response to this assumed situation, the psalmist says that it is the righteous, not the wicked, who are to be considered "happy." The psalm envisions a coming time when...
- Judgment will come (cf. v. 5)
- YHWH will separate the wicked from the righteous (like chaff from grain) (cf. vv. 4-5)
- YHWH will remove the wicked from the land (just as wind blows away the chaff) (cf. vv. 4-5)
- The righteous alone will possess the land (see esp. Ps 37 as in many ways echoing the themes of Ps 1)
- The righteous will flourish like trees in YHWH's garden (cf. Ps 92, which also echoes the themes of Ps 1)
In order to fully appreciate this "story" and understand the psalm, some background information is necessary:
- People declare someone to be "happy" (אַשְׁרֵי) when they admire that person's condition and consider it to be admirable and desirable (cf. Janzen 1965, 215-226; SDBH). For example, when the Queen of Sheba saw the wealth and wisdom and King Solomon, she exclaimed, "Happy (אַשְׁרֵי) are your men! Happy are your servants, who continually stand before you and hear your wisdom!" (1 Kgs 10:8, ESV).
- When wicked people flourish, others are tempted to declare them "happy." For example, Malachi (which occurs immediately before Ps 1 in the order of the Hebrew canon) says, “You have said, ‘It is futile to serve God. What do we gain by carrying out his requirements and going about like mourners before the Lord Almighty? But now we call the arrogant blessed. Certainly evildoers prosper, and even when they put God to the test, they get away with it’” (Mal 3:14-15, NIV; cf. Jer 12:1; Ps 73).
- YHWH is the judge of all the earth (Gen 18:25), and the job of a just judge is to acquit the righteous/innocent (צַדִּיק) and condemn the wicked/guilty (רָשָׁע) (see Deut 25:1).
- "In winnowing, grain is threshed in order to separate the kernel of grain from the husk and straw. The mixture is thrown into the air with a winnowing fork or shovel. The wind blows the light husks away, the heavier straw falls near the edge of the threshing floor, and the grain falls back to the floor to be collected. Both the light husks and the heavier straw are referred to in the words translated 'chaff' in the Bible" (Ryken et al. ed. 1998, 136).
- The place of YHWH's life-giving presence is depicted as a garden paradise (Gen 2; Ezek 47:12) in which the righteous grow like trees (Pss 52:10; 92:13-15; cf. Creach 1999).
Background situation
The background situation is the series of events leading up to the time in which the psalm is spoken. These are taken from the story triangle – whatever lies to the left of the star icon.
Expanded Paraphrase
The expanded paraphrase seeks to capture the implicit information within the text and make it explicit for readers today. It is based on the CBC translation and uses italic text to provide the most salient background information, presuppositions, entailments, and inferences.
| Expanded paraphrase legend | |
|---|---|
| Close but Clear (CBC) translation | The CBC, our close but clear translation of the Hebrew, is represented in bold text. |
| Assumptions | Assumptions which provide background information, presuppositions, entailments, and inferences are represented in italics. |
| Text (Hebrew) | Verse | Expanded Paraphrase |
|---|---|---|
| אַ֥שְֽׁרֵי־הָאִ֗ישׁ אֲשֶׁ֤ר׀ לֹ֥א הָלַךְ֮ בַּעֲצַ֪ת רְשָׁ֫עִ֥ים וּבְדֶ֣רֶךְ חַ֭טָּאִים לֹ֥א עָמָ֑ד וּבְמוֹשַׁ֥ב לֵ֝צִ֗ים לֹ֣א יָשָֽׁב׃ | 1 | When someone's position in life is admirable and desirable, that person is declared "happy" (cf. 1 Kgs 10:8). Wicked people are sometimes declared "happy," since their position in life can seem admirable and desirable (cf. Mal 3:14-15). But I do not call the wicked "happy." Instead, I say, Happy is the one who, by the end of life's journey, has not walked in the counsel of wicked people and lived his life according to what wicked people say should or should not be done, has not taken a stand in the way of sinful people and committed to living a sinful lifestyle, and has not settled in the dwelling place of insolent people and adopted the character of an insolent person who mocks YHWH's instruction and those who follow it. |
| כִּ֤י אִ֥ם בְּתוֹרַ֥ת יְהוָ֗ה חֶ֫פְצ֥וֹ וּֽבְתוֹרָת֥וֹ יֶהְגֶּ֗ה יוֹמָ֥ם וָלָֽיְלָה׃ | 2 | Instead of receiving instruction for life's journey from wicked people, he receives instruction from YHWH. And his delight is in YHWH's instruction, and, because he delights in it, he meditates on his instruction day and night. And so he lives life's journey according to YHWH's instruction, walking on the way of the righteous and forming a character shaped by YHWH's instruction. |
| וְֽהָיָ֗ה כְּעֵץ֮ שָׁת֪וּל עַֽל־פַּלְגֵ֫י מָ֥יִם אֲשֶׁ֤ר פִּרְי֨וֹ ׀ יִתֵּ֬ן בְּעִתּ֗וֹ וְעָלֵ֥הוּ לֹֽא־יִבּ֑וֹל וְכֹ֖ל אֲשֶׁר־יַעֲשֶׂ֣ה יַצְלִֽיחַ׃ | 3 | And YHWH's instruction leads him ultimately to life in YHWH's life-giving presence, symbolized by the Garden of Eden (cf. Gen 2; Ps 36:8-10). And so I say of the person who rejects wickedness and chooses to follow YHWH's instruction that he will become like a life-giving tree in YHWH's garden (cf. Pss 52:10; 92:13-15; Ezek 47:12), a tree that has been removed from a waterless place, where it could not flourish, and transplanted by YHWH on water channels which YHWH dug to irrigate the trees in his garden. These water channels represent YHWH's instruction, which daily nourishes a person so that he becomes like a well-watered tree that gives its fruit in its season for others to eat and enjoy, and whose leaves, a source of shade and healing (cf. Ezek 47:12) do not wither. And he (i.e., the person, but ultimately, YHWH) will cause all that he does to flourish just as a healthy tree flourishes . |
| לֹא־כֵ֥ן הָרְשָׁעִ֑ים כִּ֥י אִם־כַּ֝מֹּ֗ץ אֲֽשֶׁר־תִּדְּפֶ֥נּוּ רֽוּחַ׃ | 4 | Not so the wicked people! Why would anyone consider them "happy"? They do not meditate on YHWH's instruction, and so they will not, in the end, flourish like trees in YHWH's garden. Instead, when the time of threshing and winnowing comes, they will be like chaff that, thrown up into the air with a winnowing fork, the wind drives away from the threshing floor. Just as chaff grows together with the grain in a field, so the wicked currently live together with the righteous. But the day is coming when YHWH will execute judgment and separate the wicked from the righteous, just as chaff is separated from grain at the harvest. |
| עַל־כֵּ֤ן ׀ לֹא־יָקֻ֣מוּ רְ֭שָׁעִים בַּמִּשְׁפָּ֑ט וְ֝חַטָּאִ֗ים בַּעֲדַ֥ת צַדִּיקִֽים׃ | 5 | Therefore, because wicked people will be like chaff that is separated from the grain and blown away, wicked people will not stand firm in the judgment. When YHWH judges between the wicked and the righteous, they will not be able to escape YHWH's verdict and sentence. Unable to stand firm, they will be "blown away," removed from the land and from YHWH's life-giving presence. And sinful people [will not be declared righteous and stand] in the group of righteous people, because YHWH is just and will never declare the guilty to be righteous. |
| כִּֽי־יוֹדֵ֣עַ יְ֭הוָה דֶּ֣רֶךְ צַדִּיקִ֑ים וְדֶ֖רֶךְ רְשָׁעִ֣ים תֹּאבֵֽד׃ | 6 | Here, then, is the reason why I declare the righteous, and not the wicked, to be "happy": Because YHWH cares for the way of righteous people, and although it can seem as though wicked people are the ones flourishing, the way of wicked people will come to an end. |
There are currently no Imagery Tables available for this psalm.
Bibliography
- Anderson, A. A. 1972. The Book of Psalms. Vol. 1. NCBC. Greenwood, SC: Attic.
- Arbez, Edward. 1945. “A Study of Psalm 1.” The Catholic Biblical Quarterly 7 (4): 398–404.
- Auffret, Pierre. 1978. “Essai sur la structure littéraire du Psaume 1.” Biblische Zeitschrift 22 (1): 26–45.
- Auffret, Pierre. 2001. “Comme un arbre ...: etude structurelle du Psaume 1.” Biblische Zeitschrift 45 (2): 256–64.
- Auvray, Paul. 1946. “Le Psaume 1.” Revue Biblique 53 (3): 365–71.
- Barbiero, Gianni. 1999. Das erste Psalmenbuch als Einheit: eine synchrone Analyse von Psalm 1-41. Österreichische biblische Studien ; Bd. 16. Frankfurt am Main: Peter Lang.
- Barthélemy, Dominique. 2005. Critique Textuelle de l’Ancien Testament. Vol. Tome 4: Psaumes. Fribourg, Switzerland: Academic Press.
- Botha, Phil. 2005. “Intertextuality and the Interpretation of Psalm 1.” OTE 18 (3): 503–20.
- Bratcher, Robert G., and William D. Reyburn. 1991. A Handbook on Psalms. UBS Handbook Series. New York: United Bible Societies.
- Briggs, Charles A., and Emilie Briggs. 1906. A Critical and Exegetical Commentary on the Book of Psalms. Vol. 1. ICC. Edinburgh: T & T Clark.
- Creach, Jerome. 1999. “Like a Tree Planted by the Temple Stream: The Portrait of the Righteous in Psalm 1:3.” The Catholic Biblical Quarterly 61:34–46.
- Jacobson, Rolf A., et al. 2014. The Book of Psalms. The New International Commentary on the Old Testament. Grand Rapids, Michigan: William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company.
- Gentry, Peter. 2024. “OT Canonical Order and the Three-Fold Division of the Talmud.” At ETS. San Diego.
- Ho, Peter C. W. 2019. The Design of the Psalter: A Macrostructural Analysis. Eugene, Oregon: Pickwick Publications.
- Hossfeld, Frank-Lothar, and Erich Zenger. 1993. Die Psalmen I: Psalm 1–50. Neue Echter Bibel. Würzburg: Echter.
- Ibn Ezra. Psalms.
- Janzen, Waldemar. 1965. “’Ašrê in the Old Testament.” The Harvard Theological Review 58 (2): 215–26.
- Keefer, Arthur Jan. 2020. “Proverbs 21:1 and Ancient Near Eastern Hydrology.” Vetus Testamentum 71 (2): 205–18.
- Kraus, Hans-Joachim. 1988. Psalms 1-59 : A Commentary. Minneapolis : Augsburg Pub. House.
- Lefebvre, Michael. 2016. “‘On His Law He Meditates’: What Is Psalm 1 Introducing?” JSOT 40 (4): 439–50.
- Lunn, Nicholas P. 2006. Word-Order Variation in Biblical Hebrew Poetry: Differentiating Pragmatics and Poetics. Paternoster Biblical Monographs. Milton Keynes: Paternoster.
- Mitchell, David Campbell. 2021. Messiah Ben Joseph. Newton Mearns, Scotland: Campbell Publications.
- O’Connor, Michael Patrick. 1980. Hebrew Verse Structure. Winona Lake, Ind: Eisenbrauns.
- Rico, Christophe. 2019. “Yaqumu: Tenir, Prévaloir, Se Relever Ou Ressusciter?: Le Psaume 1,5 a La Lumiere de La Reception Ancienne.” Revue Biblique 126 (4): 497–520.
- Rogerson, J. W., and J. W. McKay. 1977. Psalms. Vol. 1. The Cambridge Bible Commentary on the New English Bible. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Rogland, Max. 2003. Alleged Non-Past Uses of Qatal in Classical Hebrew. Assen, The Netherlands: Royal van Gorcum.
- Ross, Allen. 2012. A Commentary on the Psalms, Volume 1: 1-41. Vol. 1. Kregel Exegetical Library. Grand Rapids: Kregel Academic & Professional.
- Ryken, Leland, Jim Wilhoit, Tremper Longman, Colin Duriez, Douglas Penney, and Daniel G. Reid, eds. 1998. Dictionary of Biblical Imagery. Downers Grove, Ill: InterVarsity Press.
- Seow, Choon Leong. 2013. “An Exquisitely Poetic Introduction to the Psalter.” Journal of Biblical Literature 132 (2): 275–93.
- Schnittjer, Gary Edward. 2021. Old Testament Use of Old Testament: A Book-by-Book Guide. Grand Rapids: HarperCollins Christian Publishing.
- van der Lugt, Pieter. 2013. Cantos and Strophes in Biblical Hebrew Poetry III: Psalms 90–150 and Psalm 1. Vol. 3. Oudtestamentische Studiën 63. Leiden: Brill.
- VanGemeren, Willem A. 1991. The Expositor’s Bible Commentary: Psalms. Edited by Tremper Longman and David E. Garland. Vol. 5. Grand Rapids: Zondervan.
- Watson, Wilfred G. E. 2005. Classical Hebrew Poetry: A Guide to Its Techniques. T & T Clark Biblical Languages. London ; New York: T & T Clark.
- Weber, B. 2006. “Psalm 1 and Its Function as a Directive into the Psalter and towards a Biblical Theology.” Old Testament Essays 19 (1): 237–60.
- Weber, Beat. 2016. Werkbuch Psalmen. 1: Die Psalmen 1 bis 72, zweite aktualisierte Auflage. Stuttgart: Verlag W. Kohlhammer.
- Willgren, David. 2018. “Why Psalms 1–2 Are Not to Be Considered a Preface to the ‘Book’ of Psalms.” ZAW 130 (3): 384–97.
- Wilson, Gerald H. 2002. Psalms. Vol. 1. NIVAC. Grand Rapids: Zondervan.
Footnotes
- ↑ Common-ground assumptions include information shared by the speaker and hearers. In our analysis, we mainly use this category for Biblical/ANE background - beliefs and practices that were widespread at this time and place. This is the background information necessary for understanding propositions that do not readily make sense to those who are so far removed from the culture in which the proposition was originally expressed.
- ↑ Local-ground assumptions are those propositions which are necessarily true if the text is true. They include both presuppositions and entailments. Presuppositions are those implicit propositions which are assumed to be true by an explicit proposition. Entailments are those propositions which are necessarily true if a proposition is true.
- ↑ Whereas local-ground assumptions are inferences which are necessarily true if the text is true, play-ground assumptions are those inferences which might be true if the text is true.